Have you ever wondered why the powerful Ottoman Empire decided to join World War 1? It wasn’t a simple choice, and the reasons behind it are both surprising and complex.
Understanding this decision helps you see how history shaped the world you live in today. You’ll discover the key motives, secret alliances, and risky moves that pulled the Ottomans into one of the deadliest conflicts in history. Keep reading, and you’ll uncover the story behind a moment that changed everything.
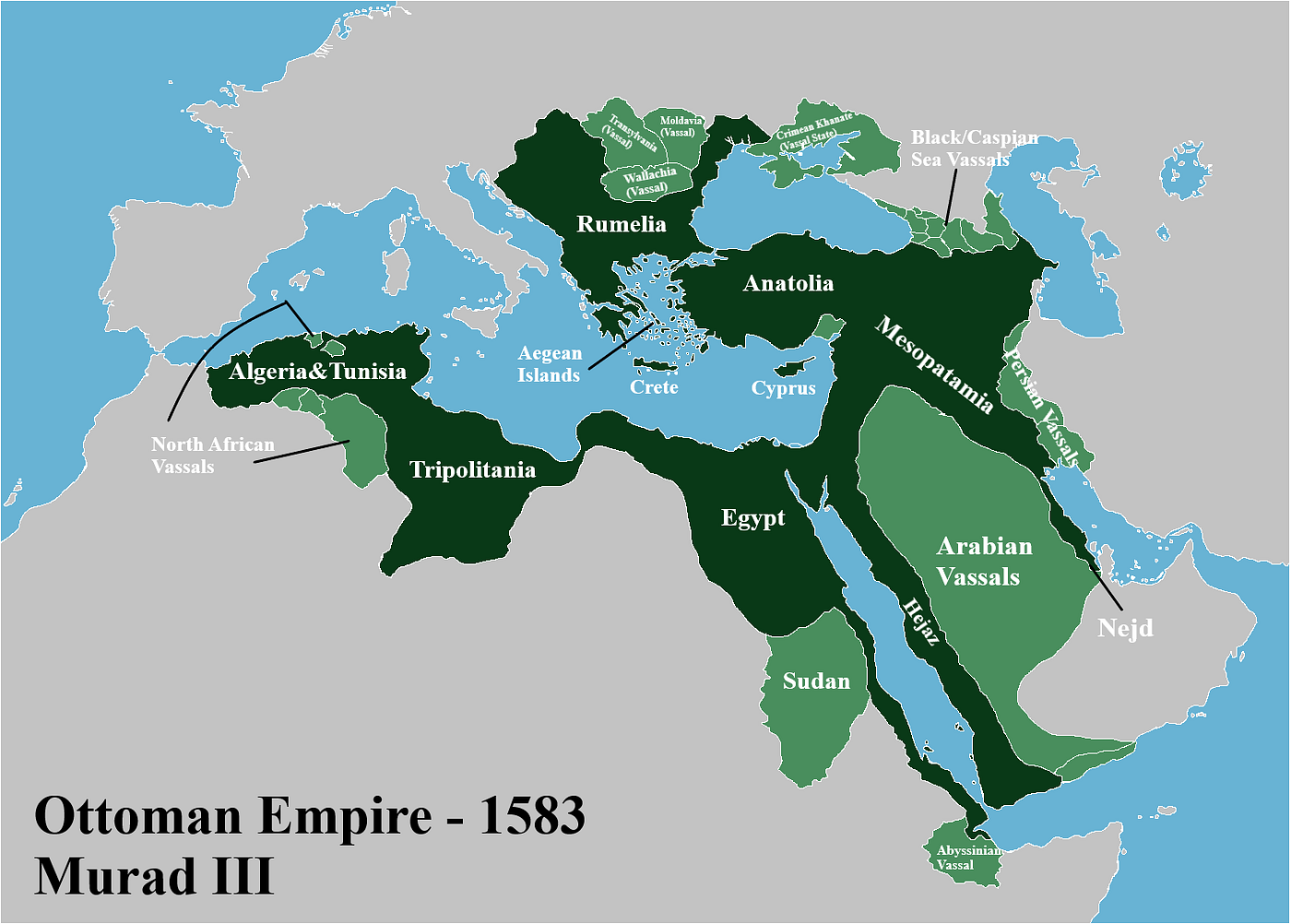
Ottoman Empire Before Ww1
The Ottoman Empire stood at a crossroads before World War I, grappling with internal challenges and external threats. Understanding its state during this period reveals why it chose to enter a global conflict. Let’s examine key aspects of the empire’s condition before the war.
Political Landscape
The empire was ruled by Sultan Mehmed V, but real power often lay with the Young Turks, a reformist group that seized control in 1908. They aimed to modernize the state and military, but their nationalist policies stirred unrest among diverse ethnic groups. This political tension weakened the empire’s unity and made its leadership eager to find strong allies.
Have you ever wondered how political instability can push a nation toward risky decisions? The Ottomans’ fragile political balance made them vulnerable to external influence and internal dissent.
Military Strength
The Ottoman military was outdated compared to European powers, despite some modernization efforts. Their army lacked sufficient training, modern equipment, and cohesive strategy. However, the empire still controlled strategic territories, including the vital Dardanelles strait, which was key for controlling naval access between the Mediterranean and Black Sea.
Imagine being in charge of an army that knows it’s behind its rivals technologically. Would you risk war to try to regain strength, or wait for reform? The Ottomans chose the former, hoping an alliance might boost their military standing.
Economic Conditions
The empire’s economy was fragile and heavily dependent on agriculture, with limited industrial development. Foreign debts had piled up, and European powers controlled many key economic sectors through concessions and investments. This economic weakness reduced the Ottomans’ ability to sustain long-term military campaigns without outside support.
Could you manage a country with shrinking resources and growing debts? The empire’s economic struggles added pressure to find allies who could provide financial and military aid.
Tensions With European Powers
The Ottoman Empire’s decision to join World War I was heavily influenced by its strained relationships with major European powers. These tensions were not new but had built up over decades, fueled by competition for territory, influence, and survival. Understanding these conflicts helps you see why the Ottomans felt pushed toward an alliance that seemed risky but necessary.
Rivalries With Russia
The Ottomans and Russia had a long history of rivalry, especially over control of the Black Sea region and the Caucasus. Russia’s ambition to expand southward threatened Ottoman territories, making trust almost impossible.
Remember how you might feel cornered if a neighbor constantly tries to take your garden space? The Ottomans felt the same about Russia’s repeated invasions and support for rebellious groups within Ottoman lands.
These ongoing disputes made the Ottomans wary of standing alone against Russian pressure during the war.
Conflicts With Britain And France
Britain and France were also key players in the Ottoman Empire’s troubles. Both powers aimed to weaken the Ottomans to gain control over strategic trade routes and resources in the Middle East.
Their backing of nationalist uprisings and territorial claims added to Ottoman insecurity. Have you ever had to deal with people undermining your plans behind your back? That’s how the Ottomans saw these European powers.
Such conflicts pushed the empire closer to Germany, hoping for protection against these European threats.
Alliance With Germany
The Ottoman Empire’s decision to join World War I alongside Germany was influenced by a complex web of strategic, military, and economic factors. The alliance with Germany wasn’t a mere coincidence but a calculated move that promised significant advantages. Understanding this alliance sheds light on the strategic maneuvers that shaped a pivotal moment in history.
Strategic Partnership
The alliance with Germany offered the Ottomans a strategic partnership that promised increased security and influence. Germany, a rising power, had advanced military technology and a robust infrastructure. This partnership aimed to counterbalance the threats posed by the Entente Powers, particularly Russia, which had territorial ambitions in Ottoman regions.
Think about it: aligning with a strong partner can often provide the necessary leverage against a formidable opponent. The Ottomans saw Germany as a gateway to modernizing their military and boosting their regional standing.
Military Cooperation
Military cooperation between the Ottomans and Germany was a cornerstone of their alliance. German military advisors and officers were integrated into the Ottoman military structure, offering training and modern tactical insights. This collaboration was intended to revitalize the Ottoman military, which had been lagging behind other European powers.
Consider the impact of having expert mentors enhance your skills—it can be a game-changer. The Ottomans hoped that German expertise would transform their forces into a formidable military machine capable of defending their vast empire.
Economic Benefits
The economic benefits of aligning with Germany were significant for the Ottoman Empire. Germany promised financial aid and investment in Ottoman infrastructure, which was in dire need of modernization. The construction of the Berlin-Baghdad railway, for instance, symbolized the economic collaboration, facilitating trade and military logistics.
Imagine the prospect of revitalizing an economy with foreign investment and cutting-edge infrastructure. This partnership with Germany was seen as a lifeline for the Ottomans, offering a pathway to economic recovery and growth.
So, what are your thoughts? Would you consider forming an alliance if it promised such strategic, military, and economic advantages? The Ottoman-German alliance was a gamble, but it was a calculated one driven by the pressing needs of the time.
Credit: medium.com
Goals Of Joining The War
The Ottoman Empire joined World War I with clear goals in mind. Leaders aimed to secure the empire’s future amid growing threats. Their decisions were driven by hopes to expand, protect, and strengthen their position globally. Understanding these goals helps explain why the Ottomans chose to enter the conflict.
Territorial Ambitions
The Ottomans wanted to regain lands lost in earlier wars. They aimed to expand their borders, especially in the Caucasus and the Middle East. Control over key regions meant more resources and strategic power. These ambitions motivated their alliance with the Central Powers.
Preserving The Empire
The empire was weak and faced internal challenges. Joining the war was seen as a way to stop further decline. Leaders hoped to unify the diverse population through a common cause. War offered a chance to strengthen control over distant provinces.
Gaining International Influence
The Ottomans sought recognition as a major power. Aligning with Germany and Austria-Hungary promised political and military support. They aimed to improve their standing in global affairs. This alliance could help negotiate better terms after the war.
Impact Of Ottoman Entry
The Ottoman Empire’s entry into World War I shifted the conflict’s scale and scope. It added new fronts and altered existing strategies. Its involvement affected not only the European theaters but also reshaped the Middle East’s political landscape. The empire’s participation had profound effects during and after the war.
Shifts In War Dynamics
The Ottomans opened new battlefronts, stretching Allied forces thin. Their control of key waterways impacted naval operations and supply routes. This forced the Allies to divert troops and resources. The Central Powers gained strategic advantages from Ottoman territories. The war’s complexity increased as a result.
Influence On Middle Eastern Front
The Ottoman Empire’s entry brought major battles to the Middle East. It led to campaigns in Gallipoli, Mesopotamia, and Palestine. These battles influenced local populations and shifted regional power balances. The conflict triggered nationalist movements among Arab peoples. The war became a catalyst for future Middle Eastern changes.
Long-term Consequences
The collapse of the Ottoman Empire followed the war’s end. New countries and borders emerged across the Middle East. The Treaty of Sèvres and later Lausanne shaped modern nation-states. Ottoman entry indirectly influenced global politics and colonial interests. Its legacy remains visible in today’s Middle East conflicts.
Credit: medium.com

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Did The Ottomans Choose To Join World War 1?
The Ottomans joined World War 1 to regain lost territories and strengthen their empire. They allied with Germany for military support and protection against Russia and the Allies.
What Role Did The Ottoman-german Alliance Play In Ww1?
The Ottoman-German alliance provided the Ottomans with weapons, military advisors, and strategic support. This partnership helped the Ottomans defend their lands and challenge Allied forces in key battles.
How Did Ottoman Entry Impact World War 1 Outcomes?
Ottoman entry expanded the war to the Middle East, opening new fronts. Their involvement prolonged the conflict and influenced the post-war division of Ottoman territories.
What Were The Main Reasons For Ottoman Distrust Of The Allies?
The Ottomans distrusted the Allies due to prior territorial losses and conflicting interests. They feared losing more land if they sided with the Allies, pushing them toward the Central Powers.
Conclusion
The Ottomans joined World War I to protect their empire and interests. They hoped to regain lost lands and gain new allies. Their choice shaped the war’s course and changed history. Understanding their reasons helps us see the bigger picture.
It shows how nations act when facing threats. This topic remains important for learning about global conflicts.





