Have you ever wondered about the religious roots of one of history’s most powerful empires? The Ottomans ruled vast lands for centuries, but were they Sunni or Shia?
Understanding this can change the way you see their culture, politics, and influence. If you want clear answers and surprising facts about the Ottoman Empire’s faith, keep reading. This article will guide you through the key details in a simple and engaging way—just for you.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Ottoman Empire Origins
The origins of the Ottoman Empire are essential to understanding its religious identity and political power. Emerging from a small principality in Anatolia, the empire grew rapidly to become a dominant force in both Europe and Asia. The early years set the foundation not only for territorial expansion but also for the religious orientation that shaped its legacy.
Founding Of The Empire
The Ottoman Empire began around the late 13th century under Osman I, a leader from a Turkic tribe. His leadership united various smaller groups, creating a strong base for expansion. The empire’s name itself comes from Osman, highlighting his role in its foundation.
Osman’s early conquests were strategic, often targeting Byzantine territories weakened by internal conflict. This approach helped the Ottomans establish a foothold in both Asia Minor and the Balkans. You might wonder how a small principality managed to grow into such a vast empire—much of this was due to Osman’s ability to attract loyal warriors and skilled administrators.
Religious Landscape In Early Ottoman Era
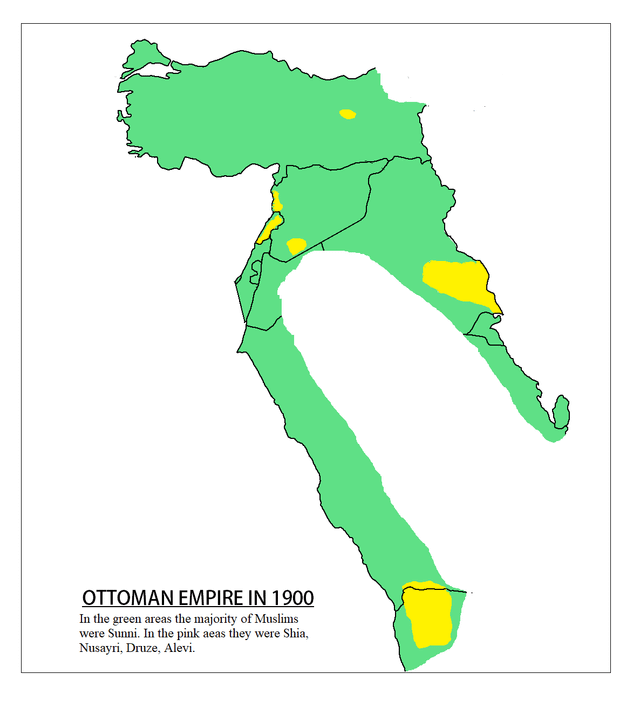
The Ottomans were Sunni Muslims, aligning with the majority sect within Islam. This Sunni identity influenced their laws, governance, and relations with neighboring states. However, the early empire was also home to diverse religious groups, including Christians and various Muslim sects.
This diversity posed challenges but also opportunities. The Ottomans often allowed religious minorities a degree of autonomy under the millet system. This practical approach helped maintain peace in a multi-ethnic empire and ensured the loyalty of different communities.
Have you ever thought about how religious identity can shape a nation’s policies? The Ottoman commitment to Sunni Islam guided their legal system and diplomatic relations, but their tolerance of other faiths was key to managing a vast and varied population.
Credit: www.academia.edu
Sunni Islam And The Ottomans
The Ottoman Empire was closely linked to Sunni Islam. This connection shaped its culture, law, and politics. Sunni Islam guided the empire’s identity and helped unify its diverse people. The Ottomans adopted Sunni beliefs and made them central to their rule.
Adoption Of Sunni Creed
The Ottomans officially embraced Sunni Islam early in their history. They followed the Hanafi school of Sunni law. This school was flexible and suited the empire’s needs. It helped them manage a wide range of peoples and traditions. The Sunni creed became the empire’s religious foundation.
Role Of Sunni Scholars
Sunni scholars held an important place in Ottoman society. They taught religious law and Islamic sciences. These scholars advised sultans and helped create laws. Their guidance ensured the empire followed Sunni principles. They also ran schools and mosques across the empire.
Sunnism In Ottoman Governance
Sunni Islam influenced Ottoman governance deeply. The sultan was seen as the protector of Sunni faith. Religious laws shaped court decisions and public policies. Sunni clerics worked with the state to maintain order. This partnership kept religion and government closely connected.
Shia Influence And Presence
The Ottoman Empire, a vast and culturally diverse realm, was predominantly Sunni. However, the presence and influence of Shia communities were significant, presenting a fascinating tapestry of religious and cultural interactions. Understanding this dynamic is crucial in appreciating the empire’s complex socio-political landscape.
Shia Communities Within The Empire
Shia communities existed in various regions of the Ottoman Empire, including parts of modern-day Iraq, Lebanon, and eastern Turkey. These communities often maintained their distinct religious practices and cultural traditions despite being in a Sunni-dominated empire. Have you ever wondered how these communities managed to preserve their identity over centuries?
Many Shia Muslims lived in relatively autonomous regions, where they could practice their beliefs freely. This autonomy allowed them to develop unique cultural identities that enriched the empire’s diversity. The resilience of these communities is a testament to their strong cultural and religious heritage.
Relations With Shia Powers
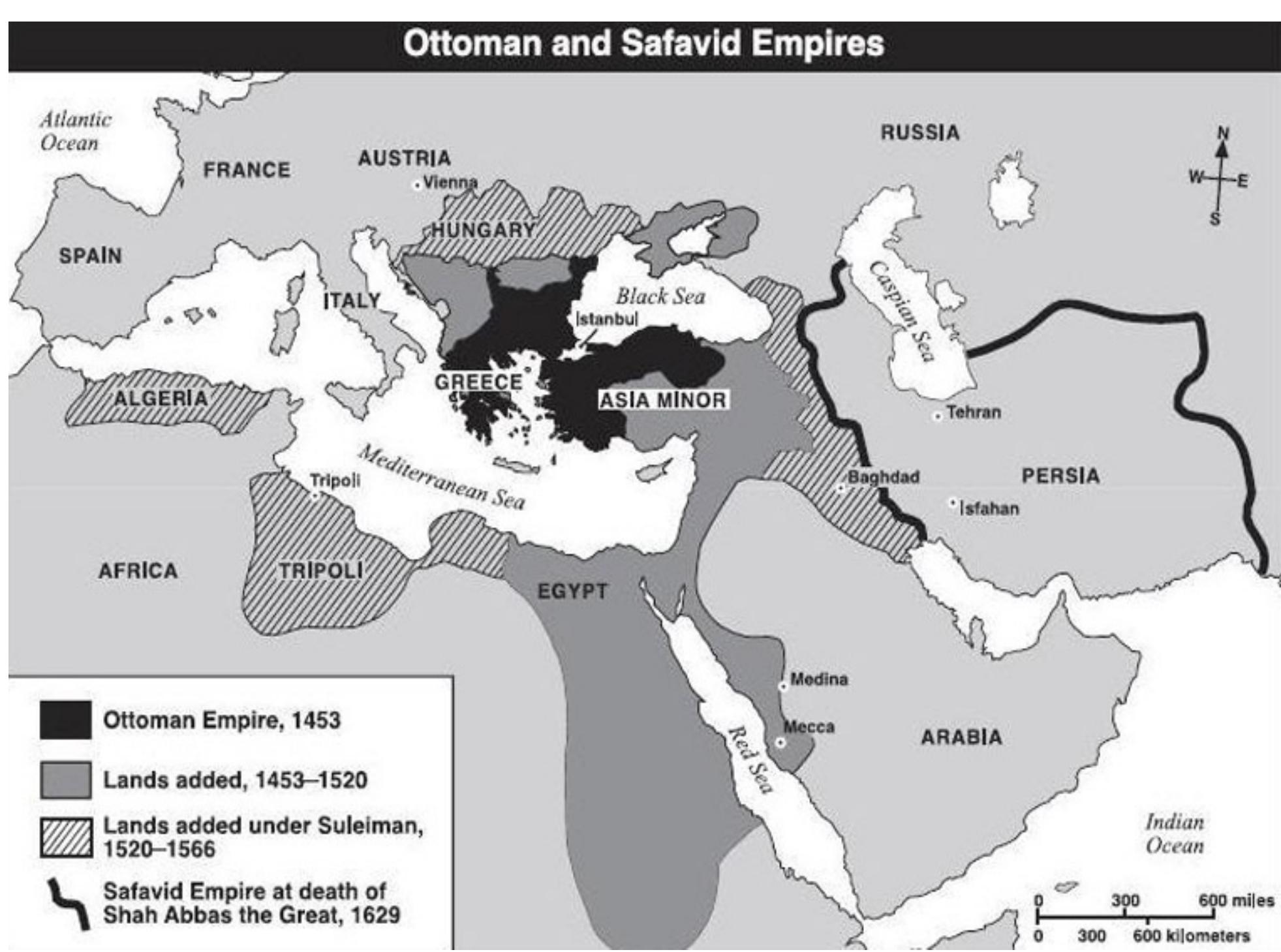
The Ottomans had a complicated relationship with Shia powers, particularly the Safavid Empire in Persia. The Safavids were a formidable Shia rival, leading to frequent conflicts and tensions. This rivalry often spilled over into the treatment of Shia communities within Ottoman territories.
Despite these tensions, there were instances of cooperation and trade between the two empires. Such interactions sometimes led to cultural exchanges that influenced both Sunni and Shia practices. How do you think these exchanges impacted the everyday lives of people within these empires?
Shia Practices And Restrictions
While Shia communities had some freedom, there were restrictions on certain practices. The Ottoman authorities often viewed Shia rituals with suspicion, fearing they could incite rebellion. This led to periodic crackdowns and limitations on public displays of Shia faith.
However, many Shia Muslims found ways to adapt their practices to avoid conflict. They often celebrated their traditions in private or in regions where they felt safer. This adaptability ensured the survival of Shia practices despite challenges. How do you think such resilience shapes a community’s identity over time?

Credit: www.wikiwand.com
Ottoman-safavid Rivalry
The Ottoman-Safavid rivalry shaped much of the political and religious landscape in the Middle East. These two empires clashed over territory, power, and religious beliefs. The Ottomans were mainly Sunni Muslims, while the Safavids followed Shia Islam. This difference deepened their conflict and created lasting effects on the region.
Religious Differences Fueling Conflict
The Ottomans supported Sunni Islam, which is the largest branch of Islam. The Safavids, however, promoted Shia Islam, especially the Twelver sect. This created a strong religious divide between them. Each empire viewed the other’s beliefs as a threat to their own authority. Religious leaders played a key role in encouraging loyalty to their empires.
Political And Military Clashes
The rivalry led to many wars and battles over control of lands. Both empires wanted to expand their borders and spread their religious influence. Key conflicts included the Battle of Chaldiran in 1514, where the Ottomans won a decisive victory. These clashes shaped the borders of modern-day Turkey, Iran, and surrounding areas.
Impact On Sectarian Identity
The conflict reinforced the sectarian identities of Sunni and Shia Muslims. In Ottoman lands, Sunni Islam remained dominant and was closely tied to the state. In Safavid territory, Shia Islam became a core part of national identity. This division affected politics, culture, and society for centuries. It still influences relations in the Middle East today.
Religious Policies Of The Ottomans
The religious policies of the Ottomans shaped their empire deeply. Their approach balanced power, faith, and society. The Ottomans were Sunni Muslims but ruled over many different religious groups. Their policies reflected both tolerance and control to maintain stability.
Tolerance And Suppression
The Ottomans allowed religious minorities to practice their faith. Christians and Jews lived under the millet system. This system gave each community some self-rule in legal and religious matters.
At the same time, the Ottomans suppressed groups seen as threats. Shia Muslims faced restrictions because the empire followed Sunni Islam. Rebellions by Shia groups were often met with harsh measures.
Role Of The Caliphate
The Ottoman sultans claimed the title of Caliph. This title made them leaders of Sunni Islam worldwide. It gave the empire religious authority and political power.
As Caliph, the sultan promoted Sunni practices and law. The role helped unify diverse peoples under a single Islamic leadership. It also justified Ottoman rule over Muslim lands.
Religious Institutions
The Ottomans supported many religious institutions like mosques and madrasas. These places educated people in Islamic law and theology. The ulema, religious scholars, advised the sultan on religious matters.
Religious leaders helped enforce Sunni orthodoxy. They also played a role in social services and justice. These institutions strengthened the Ottoman state’s control over religion and society.
Legacy Of Ottoman Sectarian Identity
The legacy of Ottoman sectarian identity shapes much of the Middle East’s religious and political landscape today. The Ottoman Empire was predominantly Sunni Muslim, and this identity influenced its governance and relations with Shia communities. The way the Ottomans managed sectarian differences left lasting impressions on societies and power structures. Understanding this legacy helps explain some modern tensions and alliances across the region.
Modern Perceptions
Many people see the Ottoman Empire as a defender of Sunni Islam. This image affects how modern Sunni groups view their history and identity. In some countries, Ottoman history is taught with a strong Sunni emphasis. Shia communities often remember the empire as a ruler that limited their influence. These differing views create varied perceptions of the Ottomans in today’s world.
Influence On Contemporary Sunni-shia Relations
The Ottoman approach to sectarianism still impacts Sunni-Shia relations. The empire favored Sunnis in political roles and religious leadership. This created a power imbalance that echoes in modern conflicts. Some Sunni states trace their authority to Ottoman traditions. Shia groups often seek greater recognition and rights, challenging old hierarchies. The legacy of Ottoman sectarian policies contributes to ongoing dialogue and disputes across the region.
Frequently Asked Questions
Were The Ottomans Sunni Or Shia Muslims?
The Ottomans were Sunni Muslims. They followed the Hanafi school of Sunni Islamic jurisprudence. This Sunni identity shaped their political and religious policies throughout their empire’s history.
Why Did The Ottomans Adopt Sunni Islam?
The Ottomans adopted Sunni Islam to unify diverse peoples. Sunni Islam helped legitimize their rule and counter Shia Safavid rivals. This religious choice strengthened their political and military power.
How Did Ottoman Sunni Beliefs Affect Their Empire?
Sunni beliefs influenced Ottoman law, education, and governance. The empire promoted Sunni scholars and Sufi orders to maintain social order. Sunni Islam was integral to Ottoman culture and administration.
Did The Ottomans Have Conflicts With Shia Groups?
Yes, the Ottomans frequently conflicted with Shia Safavids. Religious differences fueled political and military rivalries. These conflicts shaped Ottoman foreign policy and border control.
Conclusion
The Ottoman Empire followed Sunni Islam. This shaped their laws and culture deeply. They ruled many lands with Sunni beliefs. Their Sunni identity influenced their relations with others. Understanding this helps explain their history better. The Sunni faith was central to their power.
It guided their leaders and people daily. Knowing this clears common confusions about the Ottomans. Sunni Islam was key to their success. Their story shows how religion can shape empires.