Have you ever wondered which countries were once part of the vast Ottoman Empire? Understanding this can change the way you see history and the world today.
The Ottoman Empire shaped cultures, borders, and traditions across many lands. By discovering the countries it included, you’ll gain insight into the rich stories behind modern nations. Keep reading to uncover the surprising reach of this powerful empire and how it still influences your life now.

Credit: uk.news.yahoo.com
Origins Of The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire began as a small principality in the late 13th century. Founded by Osman I, it grew in a region that is now part of Turkey. The empire’s origins lie in a mix of tribal leadership and strategic conquests. These early stages set the foundation for a vast empire that lasted over six centuries.
Early Expansion
The Ottomans first expanded into Byzantine lands. They used skilled warriors and smart diplomacy. Their control spread across northwest Anatolia. This growth attracted more tribes to join their cause. The early expansion created a strong base for future conquests.
Key Conquests
One of the crucial conquests was the capture of Bursa in 1326. It became the first major Ottoman capital. Later, the fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked a turning point. This victory gave the Ottomans control over a vital trade route. The empire then expanded into the Balkans and the Middle East.
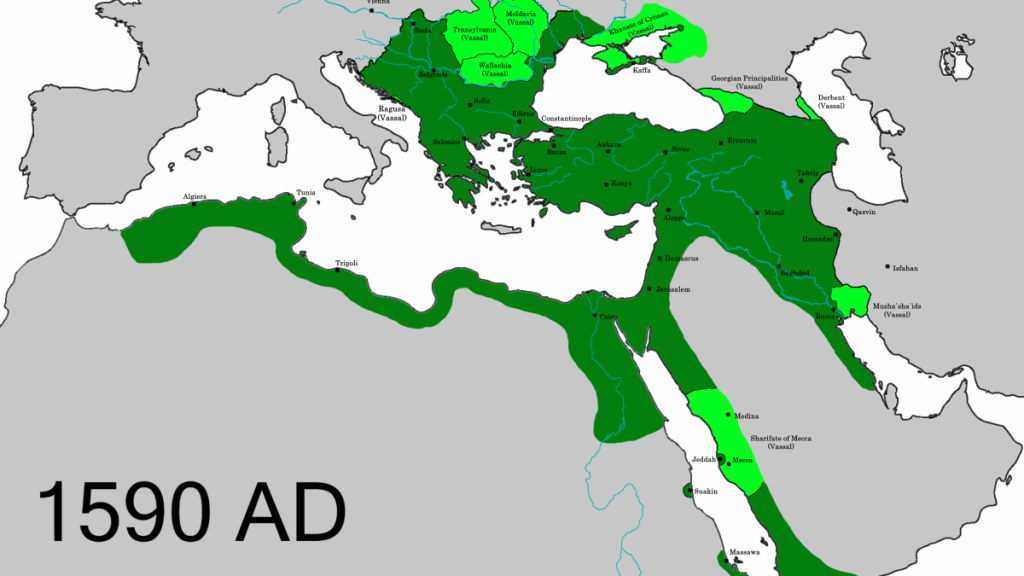
Territorial Growth At Its Peak
The Ottoman Empire reached its greatest size between the 16th and 17th centuries. Its territory spread across three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. This vast land brought many cultures and peoples under one rule. The empire controlled key cities and trade routes. Its power shaped history in many regions.
Europe
In Europe, the Ottoman Empire ruled large parts of the Balkans. Countries like Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Romania were under Ottoman control. The empire also held Hungary and parts of Ukraine for a time. Istanbul, formerly Constantinople, served as the capital and a major cultural hub.
Asia
Asia was home to some of the empire’s richest lands. The Ottomans controlled most of modern-day Turkey and extended into the Middle East. This included Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, and Palestine. The empire also held parts of the Arabian Peninsula, including Mecca and Medina.
Africa
In Africa, the Ottoman Empire ruled the northern coast. This included Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, and Algeria. Control over these areas helped the empire dominate Mediterranean trade. The empire also influenced parts of Sudan and the Red Sea coast.
Modern Countries Formed From Ottoman Lands
Many modern countries like Turkey, Greece, Egypt, and Iraq once belonged to the Ottoman Empire. This empire covered parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa for centuries. It shaped the history and culture of these regions deeply.
Understanding the modern countries formed from the vast expanse of the Ottoman Empire can offer you a fresh perspective on today’s geopolitical landscape. The Ottoman Empire, at its peak, spanned three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. This colossal empire has left a lasting imprint on the cultural, political, and social fabric of numerous nations. Today, the lands that were once under Ottoman rule are home to a diverse array of countries, each with its unique identity and history.Balkans
The Balkans region was a significant part of the Ottoman Empire for centuries. Modern countries such as Greece, Bulgaria, and Serbia once found themselves under Ottoman control. You might find it interesting to explore how the Ottoman legacy still influences the architecture and culture in cities like Sarajevo or Belgrade. The Balkan nations, rich with history, have emerged as vibrant states, each boasting a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences. Consider how the Ottoman period contributed to the cultural tapestry you see today when visiting this region.Middle East
The Middle East was the heart of the Ottoman Empire, with its capital, Istanbul, straddling the line between Europe and Asia. Modern countries like Turkey, Iraq, and Syria were integral components of the empire. You might wonder how the Ottoman administrative systems have shaped the governance models in these nations today. This region’s complex history is evident in the way ancient traditions coexist with modern developments. When you visit, pay attention to how the Ottoman legacy is visible in language, food, and customs.North Africa
North Africa’s ties to the Ottoman Empire are often overlooked, yet they are significant. Countries such as Egypt, Libya, and Tunisia were once part of this vast empire. As you explore this region, you might notice how Ottoman influence is still visible in local architecture and art. The blending of Ottoman and North African cultures has created a unique heritage that continues to attract interest. Reflect on how this historical connection influences the cultural dynamics you observe in North African countries today. By examining these regions, you gain valuable insights into how the Ottoman Empire’s legacy continues to shape the world. What traces of this historical empire do you see in your own travels? How does understanding this legacy enhance your appreciation of these diverse cultures?Impact On Present-day Borders
The Ottoman Empire’s vast reach shaped many of today’s national borders. Its territories spanned three continents, influencing political boundaries that still exist. Understanding this impact helps you see how history continues to affect current geopolitics and cultural identities.
Legacy In Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe was deeply molded by centuries of Ottoman rule. Countries like Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Romania experienced shifts in borders and populations. You can still notice Ottoman architecture, customs, and place names in these areas.
The empire’s administrative divisions laid groundwork for many modern states. Ethnic and religious diversity in the region often traces back to Ottoman policies. Have you ever wondered why these countries have such complex cultural mosaics?
Influence In Western Asia
Modern-day Turkey, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Jordan were once Ottoman provinces. The empire’s collapse after World War I led to new borders drawn by foreign powers. These artificial lines sometimes ignored ethnic or tribal realities, causing ongoing conflicts.
Understanding Ottoman governance helps explain current tensions and alliances. For instance, the city of Istanbul remains a key cultural and economic hub due to its Ottoman heritage. How do you think history influences today’s political disputes here?
North African States
Libya, Egypt, Tunisia, and Algeria were part of the Ottoman realm, though with varying degrees of control. The empire’s influence contributed to the spread of administrative practices and legal codes. Ottoman forts and mosques still stand as reminders of this period.
Today’s borders in North Africa reflect both Ottoman legacies and later European colonization. You might notice shared cultural elements like cuisine and language that link these countries back to the empire. What role do you think these historical ties play in regional cooperation today?
Key Provinces And Regions
The Ottoman Empire spanned a vast area covering diverse lands and cultures. Its power rested on key provinces and regions that shaped its history. These areas were centers of trade, culture, and military strength. Understanding these provinces helps to grasp the empire’s influence on world history.
Anatolia
Anatolia formed the empire’s core. It is modern-day Turkey. This region had rich farmland and important cities like Istanbul and Ankara. Anatolia served as the empire’s political and economic heart. It connected Asia and Europe, making it a vital hub for trade.
Levant
The Levant included parts of today’s Syria, Lebanon, Israel, and Jordan. This region was famous for ancient cities and religious sites. It was a crossroads for different cultures and peoples. The Ottomans controlled important ports and trade routes here.
Maghreb
Maghreb covered North African lands such as Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya. These provinces gave the empire access to the Mediterranean Sea. The area was rich in resources and trade opportunities. The Ottomans used it to expand their influence in Africa and Europe.

Credit: owlcation.com
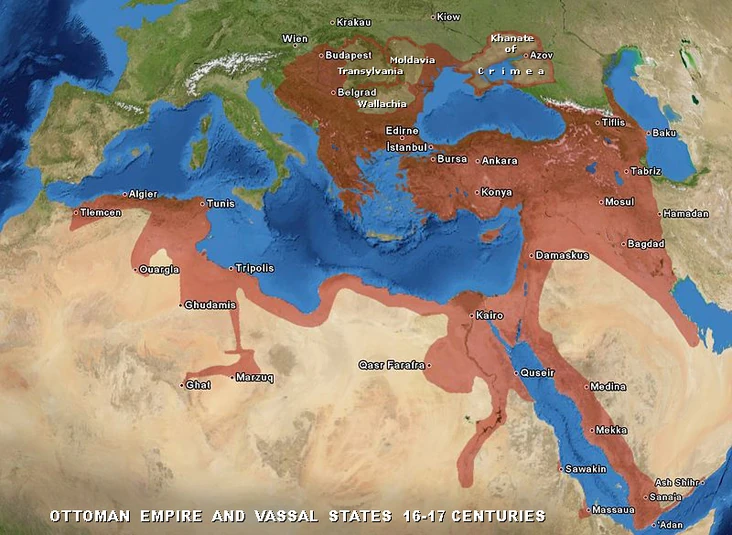
Decline And Territorial Losses
The Ottoman Empire once spanned three continents, controlling vast lands across Europe, Asia, and Africa. However, by the 19th and early 20th centuries, this powerful empire faced significant decline and territorial losses. Understanding these losses helps you grasp how the modern borders of many countries emerged from Ottoman rule.
European Wars
The Ottoman Empire clashed repeatedly with European powers, leading to costly wars that drained its resources. Battles like the Great Turkish War and the Crimean War chipped away at its control over key territories.
Each defeat forced the empire to cede land to rising European states, such as Austria-Hungary and Russia. Can you imagine how losing such important regions affected the empire’s economy and morale?
Nationalist Movements
Within the empire’s diverse population, nationalist movements gained strength, demanding independence. Groups like the Greeks, Serbs, and Armenians pushed for their own nations.
This internal pressure accelerated the empire’s fragmentation, as it struggled to maintain control over distant provinces. If you lived in that era, how would you have reacted to these calls for self-rule?
Final Dissolution
The empire’s last blow came during and after World War I, when Allied forces dismantled its remaining territories. The Treaty of Sèvres and later the Treaty of Lausanne formalized the empire’s end.
Modern countries such as Turkey, Iraq, Syria, and others emerged from the former Ottoman lands. This final dissolution reshaped the map in ways that still influence global politics today.
Credit: historica.fandom.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Countries Were Part Of The Ottoman Empire?
The Ottoman Empire included modern Turkey, Greece, Bulgaria, Egypt, Syria, Iraq, and parts of the Balkans. Its reach expanded across Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa at its peak.
When Did The Ottoman Empire Control These Countries?
The empire existed from 1299 to 1922, controlling various regions at different times. Its peak territorial extent was during the 16th and 17th centuries under Suleiman the Magnificent.
How Did The Ottoman Empire Influence These Countries?
The Ottomans shaped culture, architecture, law, and trade in their territories. Many local customs blended with Ottoman traditions, impacting language, cuisine, and governance.
Why Did The Ottoman Empire Lose Its Territories?
Loss of territories resulted from military defeats, nationalist movements, and European colonization pressures. The empire gradually shrank, culminating in its dissolution after World War I.
Conclusion
The Ottoman Empire ruled many lands across three continents. It included parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Countries like Turkey, Egypt, Greece, and Iraq were once under its control. This empire shaped cultures and history in these regions. Learning about these countries helps us understand the past better.
The Ottoman legacy still influences many people today. History connects us all.