Have you ever wondered which countries were once part of the vast Ottoman Empire? Understanding this can change the way you see history and the world map today.
The Ottoman Empire shaped cultures, languages, and borders across three continents. Knowing which lands it ruled helps you connect the past to the present in a powerful way. Keep reading, and you’ll discover surprising facts about the countries that shared this incredible legacy with the empire.
Your curiosity is about to be rewarded!

Credit: owlcation.com
Origins Of The Ottoman Empire
The origins of the Ottoman Empire reveal a story of ambition, strategy, and cultural blending. It all began in a small region of Anatolia, where a group of Turkish tribes united under a single leader. This unity set the stage for what would become one of the most powerful empires in history.
The Early Beginnings In Anatolia
The Ottoman Empire started in the late 13th century in northwestern Anatolia, near the Byzantine Empire’s borders. Osman I, the empire’s founder, led a small principality called the Beylik of Osman. His leadership turned this modest territory into a growing power.
Osman’s success came from his ability to unite various Turkic tribes and form alliances with local groups. This cooperation helped him expand his territory steadily. Have you ever thought how a small community’s unity can lead to significant influence?
Influence Of The Seljuk Turks And Mongol Invasions
The Seljuk Turks had ruled much of Anatolia before the Ottomans emerged. Their decline left a power vacuum that Osman and his successors filled. Meanwhile, Mongol invasions disrupted the region, causing many displaced peoples to seek protection under new leaders like Osman.
This chaotic environment allowed the Ottomans to gain followers and land quickly. It also shaped their military tactics and governance style. Understanding this context helps you see how external pressures can create opportunities for emerging powers.
Strategic Location And Expansion Opportunities
The Ottoman homeland was at a crossroads between Europe and Asia. This position gave them access to important trade routes and cultural exchanges. It also placed them on the front line against the Byzantine Empire, which they eventually conquered.
Controlling these routes boosted the Ottomans’ economy and military power. It also made them a key player in regional politics. Have you noticed how geography often influences a nation’s rise or fall?
Expansion Across Continents
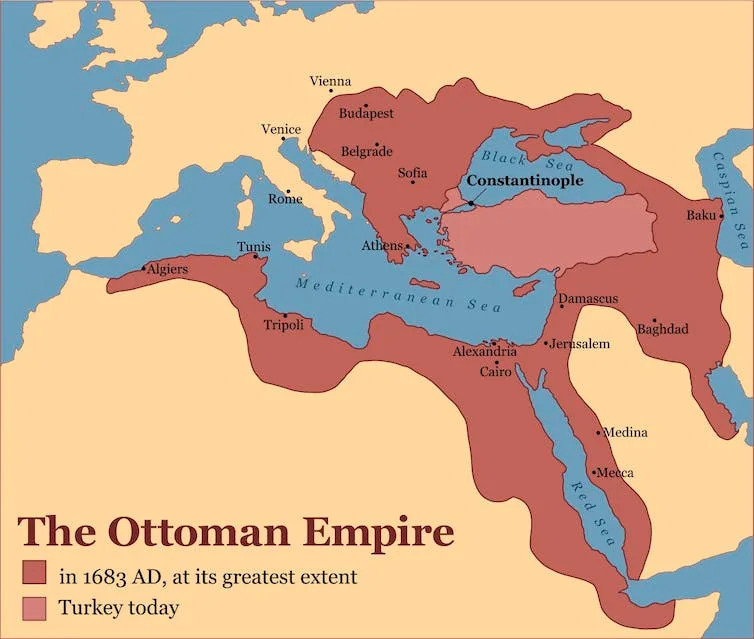
The Ottoman Empire’s expansion across continents is a fascinating story of strategic conquests and cultural blending. This vast empire stretched over Europe, Asia, and Africa, connecting diverse peoples and lands. Understanding which countries were part of the empire helps you see the scale of its influence and the legacy it left behind.
Europe
In Europe, the Ottoman Empire controlled large areas of the Balkans. Countries like Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Romania were under Ottoman rule for centuries. Istanbul, formerly Constantinople, served as a key European capital for the empire.
Think about how this shaped the cultural and architectural landscape you see in these countries today. Ottoman rule introduced new traditions, legal systems, and trade routes that still impact the region.
Asia
Asia was home to some of the empire’s most important territories. Modern-day Turkey was the heart of the empire, but it also included parts of the Middle East such as Iraq, Syria, and Palestine.
The empire’s control in Asia allowed it to connect with ancient trade routes like the Silk Road. This helped spread goods, ideas, and religions across continents, influencing your world in ways you might not expect.
Africa
In Africa, the Ottoman Empire ruled over Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, and Algeria. These regions were critical for controlling Mediterranean trade and access to African resources.
Have you ever considered how Ottoman governance affected local cultures and economies in North Africa? Their presence linked Africa more closely to European and Asian markets.
Key Territories In Europe
Several European countries were part of the Ottoman Empire, including Greece, Bulgaria, and Hungary. These territories shaped much of the region’s history and culture under Ottoman rule. Many borders and cities still reflect this past today.
The Ottoman Empire, at its peak, was a sprawling realm that stretched across three continents, including Europe. This vast empire played a pivotal role in shaping the history and culture of numerous European territories. Understanding the key territories that were part of the Ottoman Empire helps illuminate the rich tapestry of Europe’s past.Balkans
The Balkans were crucial to the Ottoman Empire, acting as a bridge between Europe and Asia. Countries like Greece, Bulgaria, and Serbia fell under Ottoman rule, leaving a lasting imprint on their architecture, cuisine, and culture. Have you ever visited the old bazaars in Sarajevo or the Ottoman-style mosques in Skopje? These are just a few testaments to the rich Ottoman legacy in the Balkans. The influence is evident even today in the region’s music, food, and festivals.Hungary And Central Europe
Hungary was a significant part of the Ottoman Empire during the 16th and 17th centuries. The Ottomans controlled large parts of Hungary and other Central European territories. This period was marked by numerous battles and a fascinating cultural exchange. The architectural styles, especially in Budapest, reflect Ottoman design elements. If you’re exploring Hungarian history, the Ottoman era offers intriguing insights into the region’s development.Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe, including parts of modern-day Romania and Ukraine, also came under Ottoman influence. The Black Sea’s strategic importance made these territories valuable. Have you considered how the Ottoman presence shaped trade routes and military strategies in this region? The empire’s legacy in Eastern Europe is visible in historical sites and the diverse cultural practices that continue to echo through time. Eastern European folklore and traditions still carry traces of the Ottoman era, offering a unique blend of influences for you to discover.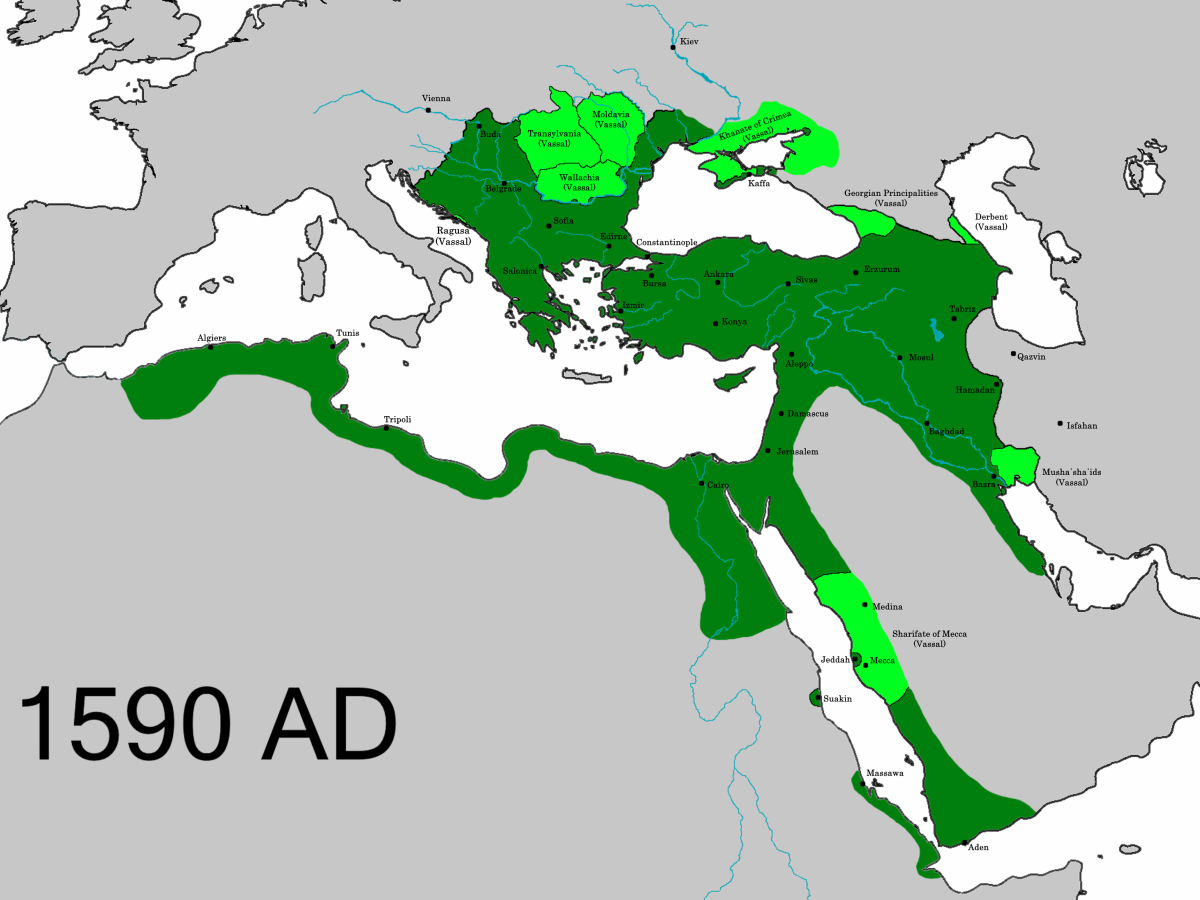
Credit: owlcation.com
Major Asian Regions
The Ottoman Empire was vast, covering many Asian regions. These areas shaped its culture and power. Understanding these regions helps to see the empire’s true size. The major Asian parts included Anatolia, the Middle East, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Caucasus. Each region had its own importance and unique role in the empire.
Anatolia And The Middle East
Anatolia, modern-day Turkey, was the empire’s heartland. It served as the main base for the sultans and their armies. The Middle East included important lands like Syria, Iraq, and Palestine. These areas were rich in history and trade. Cities like Damascus and Baghdad thrived under Ottoman control.
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula was crucial for trade routes and religious sites. The Ottomans controlled parts of modern Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and the Gulf states. Mecca and Medina, Islam’s holiest cities, were under Ottoman protection. This gave the empire great religious influence across the Muslim world.
Caucasus
The Caucasus region lies between the Black and Caspian Seas. It included modern Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Ottomans often fought for control here with Persia and Russia. This region was important for its strategic location and diverse peoples. It added to the empire’s cultural richness and military reach.
African Provinces
The Ottoman Empire stretched across continents, and its African provinces played a significant role in its vast reach. These regions were diverse, rich in culture, and strategically important for trade and military strength. Understanding these provinces helps you see how the empire managed to control such a wide area and influence various cultures.
North Africa
North Africa was a crucial part of the Ottoman Empire, including modern-day countries like Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and parts of Morocco. The Ottomans controlled key coastal cities such as Cairo, Tripoli, and Algiers, which were important trade hubs connecting Africa to Europe and the Middle East.
Egypt stood out as a jewel in the empire, thanks to the Nile River and its fertile lands. You might find it interesting that the Ottomans improved administrative systems here, which helped maintain order and boost agriculture. This control allowed the empire to secure its southern borders and maintain access to African goods.
Horn Of Africa
The Horn of Africa, covering areas of modern-day Somalia and Eritrea, was another strategic region under Ottoman influence. Though the empire’s control here was less direct, it maintained alliances and outposts along the coast to protect its trade routes in the Red Sea.
This region’s importance often goes unnoticed, but it served as a gateway for Ottoman ships traveling between the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean. If you think about the challenges of navigating these waters, the empire’s presence here was a smart move to safeguard commerce and military movements.
Important Cities Under Ottoman Rule
The Ottoman Empire controlled many important cities across three continents. These cities served as political, cultural, and economic centers. Each city played a unique role in shaping the empire’s history. They were hubs for trade, art, and governance.
Exploring these cities reveals the vast reach and diversity of the Ottoman Empire. Their legacy still influences the regions today.
Constantinople (istanbul)
Constantinople was the heart of the Ottoman Empire. It became Istanbul after the Ottoman conquest in 1453. The city was a major trade link between Europe and Asia. It housed the imperial palace, mosques, and markets. The Hagia Sophia was transformed into a mosque here.
Alexandria
Alexandria was a key port city on the Mediterranean Sea. It connected the empire to Africa and the Middle East. The city thrived on commerce and cultural exchange. Ottoman rule boosted its importance in regional trade networks.
Baghdad
Baghdad was an important center in the empire’s eastern region. It was known for its learning and culture. The city linked the Ottoman Empire to Persia and Central Asia. Baghdad served as a military and administrative hub.
Belgrade
Belgrade was a strategic fortress city in the Balkans. It guarded the empire’s European borders. The city changed hands several times during conflicts. Ottoman rule left strong architectural and cultural marks in Belgrade.
Damascus
Damascus was a vital city in the Levant region. It was famous for its history and craftsmanship. The Ottomans used it as a regional capital. Damascus was a center for religious and commercial activities.
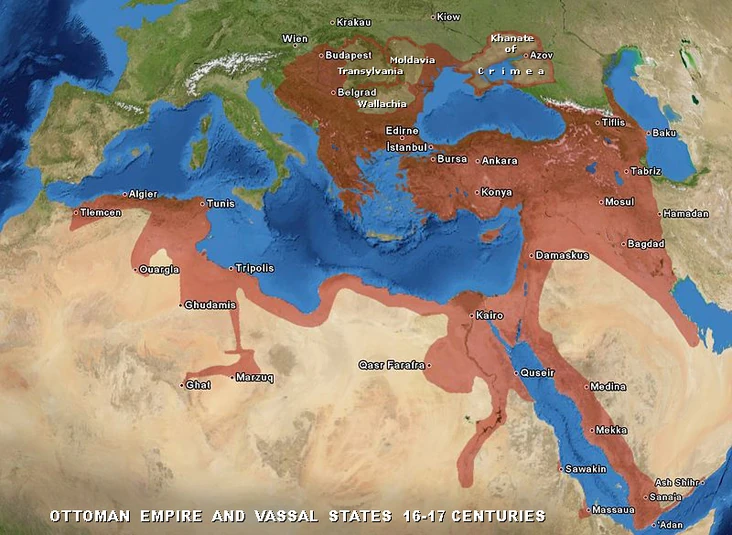
Legacy Of Ottoman Territories Today
The Ottoman Empire once covered vast lands across three continents. Its legacy still shapes the modern world in many ways. The territories it ruled are now home to several independent countries. These nations carry cultural and historical marks from centuries under Ottoman rule.
Modern Countries Formed
- Turkey
- Greece
- Bulgaria
- Serbia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- North Macedonia
- Albania
- Montenegro
- Croatia
- Romania (parts)
- Hungary (parts)
- Syria
- Lebanon
- Israel
- Palestine
- Jordan
- Iraq
- Saudi Arabia (parts)
- Egypt
- Libya
- Tunisia
- Algeria (parts)
These countries emerged after the empire’s fall in the early 20th century. Borders changed, but Ottoman influences remain visible.
Cultural Influences
Ottoman culture blends many traditions from Europe, Asia, and Africa. Architecture, language, and cuisine show this mix clearly.
- Ottoman-style mosques and palaces still stand in many cities.
- Turkish words appear in Balkan languages and Arabic dialects.
- Popular dishes like baklava and kebabs spread across former territories.
- Music and dance traditions share Ottoman roots.
- Legal and administrative systems borrowed Ottoman models for decades.
The empire’s legacy remains a common thread linking diverse peoples. It shapes identities and cultural expressions today.
Credit: historica.fandom.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Countries Were Part Of The Ottoman Empire?
The Ottoman Empire included modern Turkey, Greece, Bulgaria, Egypt, Syria, Iraq, and parts of the Balkans. It spanned three continents at its peak.
When Did The Ottoman Empire Control These Countries?
The empire controlled these regions mainly between the 14th and early 20th centuries, ending officially in 1922 after World War I.
How Did The Ottoman Empire Influence Its Territories?
The empire shaped local cultures, laws, architecture, and trade. It spread Islam and Ottoman governance systems across its lands.
Why Did The Ottoman Empire Lose Its Territories?
Loss came from military defeats, nationalist uprisings, and European colonialism. World War I dealt the final blow, leading to empire dissolution.
Conclusion
The Ottoman Empire once ruled many lands across three continents. Countries in Europe, Asia, and Africa were part of it. This empire shaped cultures, languages, and histories in these regions. Its influence still shows in traditions and buildings today. Understanding which countries belonged helps us learn world history better.
The story of the Ottoman Empire is complex but fascinating. It reminds us how connected the world has always been.