Have you ever stopped to think about what really happens when ventilation is inadequate during Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)? If you’re involved in emergency care or training, understanding this can be the difference between life and death for a child.
Poor ventilation doesn’t just mean less oxygen—it can trigger a chain reaction that affects the heart, brain, and overall survival chances. Keep reading to uncover exactly why proper ventilation matters so much and how you can spot and fix problems before it’s too late.
Your knowledge here could save a young life.
Credit: www.aclsmedicaltraining.com
Signs Of Poor Ventilation
Recognizing the signs of poor ventilation in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) is crucial for timely intervention. When ventilation is inadequate, the body struggles to get enough oxygen and remove carbon dioxide, leading to noticeable symptoms. Paying attention to these signs helps you act quickly and potentially save a life.
Physical Symptoms In Patients
Patients with poor ventilation often show clear physical signs. You might notice rapid or shallow breathing, which means the lungs aren’t exchanging air effectively.
Other symptoms include cyanosis—bluish lips or fingertips—indicating low oxygen levels in the blood. Watch for nasal flaring and use of accessory muscles in the neck or chest, which show the patient is working harder to breathe.
Changes In Vital Signs
Vital signs provide key clues about ventilation status. An increased heart rate often signals distress as the body tries to compensate for low oxygen.
Similarly, abnormal blood pressure, either too high or too low, can indicate worsening respiratory function. Oxygen saturation levels dropping below normal ranges is a direct sign of inadequate ventilation that you can monitor with a pulse oximeter.
Altered Mental Status
Poor ventilation can affect the brain quickly. Patients may become restless, confused, or lethargic as their brain cells receive less oxygen.
In more severe cases, you might see decreased responsiveness or even unconsciousness. If you notice any change in alertness, think about possible ventilation problems and act immediately.
Immediate Consequences
Inadequate ventilation triggers immediate effects that can quickly put your health at risk. These consequences happen fast and impact how your body handles oxygen and carbon dioxide. Recognizing these changes early can help you take action before the situation worsens.
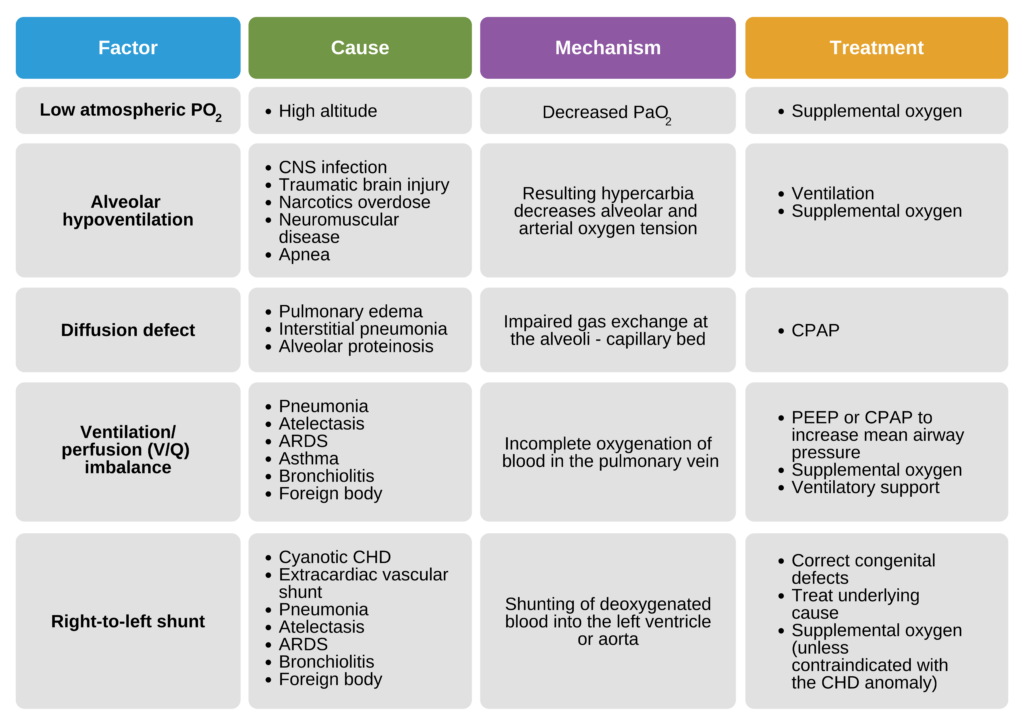
Hypoxia And Oxygen Deficiency
Hypoxia occurs when your body doesn’t get enough oxygen. This shortage affects your brain, muscles, and vital organs, making you feel dizzy, confused, or weak.
Imagine trying to run a marathon while holding your breath—your muscles and brain simply can’t perform well without oxygen. If you notice shortness of breath or unusual fatigue, it could be a sign that ventilation isn’t adequate.
Carbon Dioxide Retention
When ventilation is poor, carbon dioxide builds up in your bloodstream. Normally, your lungs remove this waste gas, but without enough airflow, it starts to accumulate.
This retention makes you feel short of breath and can cause headaches or a sense of confusion. Have you ever felt foggy-headed after being in a stuffy room? That’s your body struggling to get rid of excess carbon dioxide.
Respiratory Acidosis
Respiratory acidosis happens when carbon dioxide buildup lowers your blood’s pH, making it more acidic. This disrupts how your cells and organs function.
The condition can lead to rapid breathing, fatigue, and even a slower heartbeat. If ventilation problems continue, respiratory acidosis becomes a serious threat that needs urgent attention.
Impact On Organ Systems
Inadequate ventilation disrupts the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. This imbalance harms multiple organ systems, affecting their ability to function properly. Oxygen is vital for cell survival and energy production. Without enough oxygen, organ systems begin to fail quickly. Understanding these impacts helps highlight the urgency of proper ventilation in pediatric advanced life support (PALS).
Brain Function And Neurological Risks
The brain needs a constant oxygen supply to work well. Low oxygen levels cause confusion, dizziness, and loss of consciousness. Prolonged oxygen shortage leads to brain damage and permanent neurological problems. Carbon dioxide build-up can increase pressure inside the skull, worsening brain injury. Early intervention is key to protecting brain function.
Cardiovascular Strain
The heart works harder when oxygen is low. It pumps faster to meet the body’s needs, causing strain. This extra effort can lead to irregular heartbeats or heart failure. Poor ventilation reduces blood oxygen, weakening heart muscles. The combination increases the risk of serious cardiovascular problems.
Effects On Other Organs
Other organs like the kidneys and liver also need oxygen to survive. Lack of oxygen causes these organs to slow down or stop working. Tissues may become damaged due to poor blood flow and oxygen delivery. This can lead to multiple organ failure if ventilation issues persist.
Common Causes Of Inadequate Ventilation
Inadequate ventilation can lead to serious health issues. Understanding the common causes is crucial for prevention. Let’s explore three main causes of inadequate ventilation.
Airway Obstruction
Airway obstruction is a frequent cause of ventilation problems. It occurs when something blocks the air passage. This can happen due to food, mucus, or even a foreign object. Ensuring a clear airway is vital for proper breathing. Regular checks help in identifying and removing obstructions early.
Equipment Malfunction
Equipment malfunction can significantly impact ventilation. Machines used for breathing support can fail. Faulty equipment may not deliver the needed air. Routine maintenance and checks are essential. This ensures that all equipment functions correctly and reliably.
Improper Ventilation Techniques
Improper ventilation techniques can cause inadequate airflow. Incorrect use of breathing devices often leads to this issue. Training and practice help in mastering correct techniques. Continuous learning is crucial for effective ventilation management.
Monitoring And Early Detection
Monitoring and early detection are crucial when ventilation is inadequate in pediatric advanced life support (PALS). Identifying signs of poor ventilation quickly can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes for young patients. Using the right tools and techniques helps you stay ahead and intervene before problems escalate.
Use Of Capnography
Capnography measures the amount of carbon dioxide in exhaled air, providing real-time feedback on ventilation effectiveness. If CO2 levels drop or rise unexpectedly, it signals a problem with breathing or airway management. Have you ever noticed how quickly capnography alerts you to subtle changes that pulse oximetry might miss?
This tool helps you confirm correct tube placement and detect issues like hypoventilation or apnea early. It’s especially useful during resuscitation, giving you immediate information to adjust ventilation without waiting for clinical signs.
Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry tracks oxygen saturation levels in the blood, offering a non-invasive way to monitor respiratory status. Low oxygen levels can indicate inadequate ventilation, but this is often a late sign. That’s why relying solely on pulse oximetry can sometimes delay critical interventions.
Using pulse oximetry alongside capnography improves your ability to detect respiratory problems faster. It’s a simple tool that you should never overlook, especially in emergency situations where every second counts.
Clinical Assessment Tools
Clinical assessment remains a key part of monitoring ventilation. Observing chest rise, listening for breath sounds, and checking for signs of distress give you essential clues about the patient’s condition. These assessments can be done quickly and repeatedly at the bedside.
Combining clinical skills with technology strengthens your detection capabilities. For example, noticing increased work of breathing alongside abnormal capnography readings signals a need for immediate action. How often do you pause to reassess your patient’s ventilation status during a critical event?

Credit: heartstartcpr.net
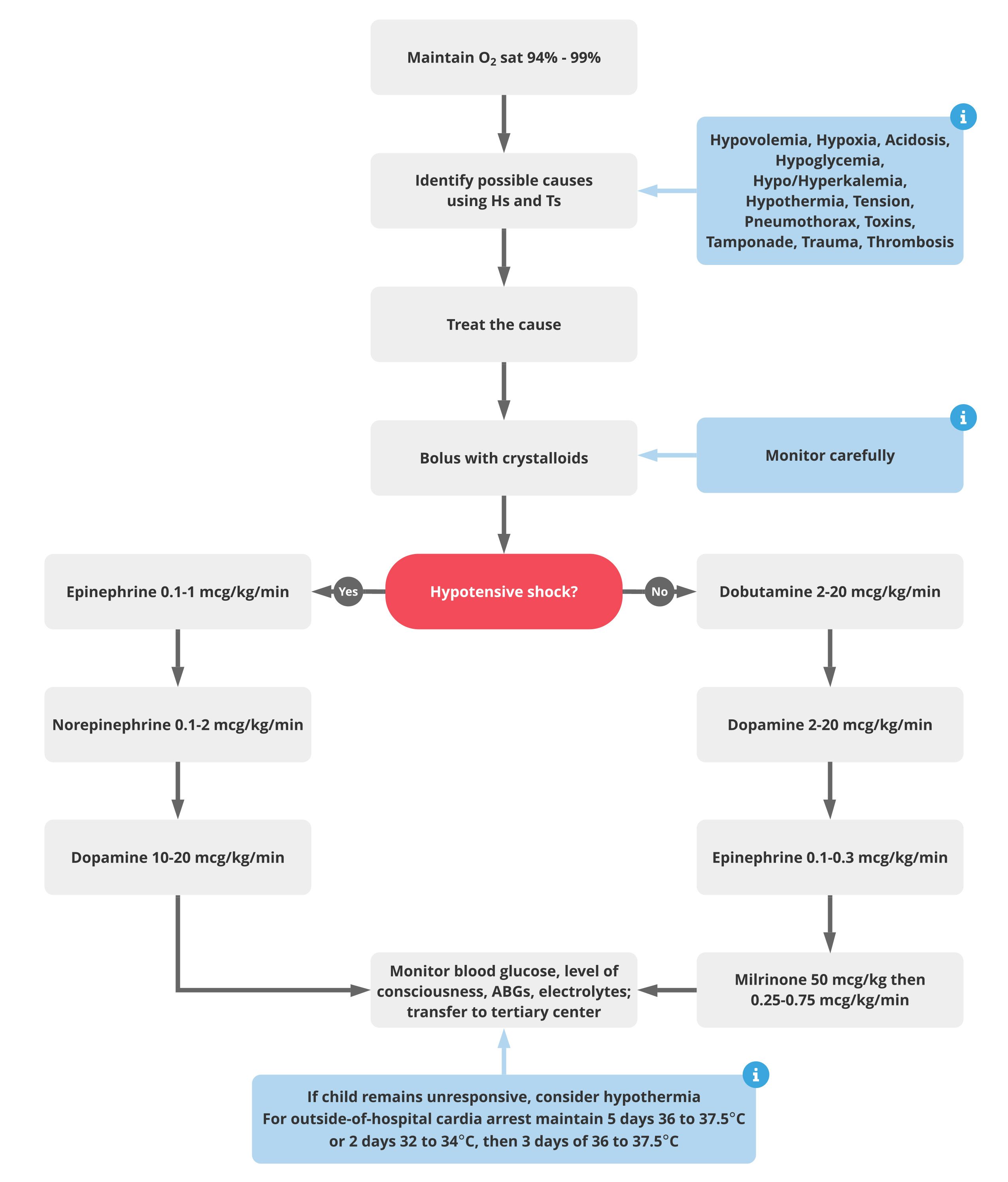
Corrective Actions And Management
Corrective actions and management are vital to address inadequate ventilation in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS). Prompt steps improve oxygen delivery and prevent complications. Healthcare providers must quickly assess the situation and apply targeted interventions.
Proper management reduces the risk of brain injury and organ damage. The goal is to restore effective breathing and maintain adequate oxygen levels. Several techniques and treatments help achieve this goal.
Adjusting Ventilation Settings
Check ventilator parameters immediately. Adjust tidal volume, respiratory rate, and pressure settings as needed. Small changes can improve ventilation efficiency. Avoid excessive pressures to reduce lung injury risk.
- Increase respiratory rate to improve carbon dioxide removal.
- Modify tidal volume to enhance oxygen exchange.
- Ensure proper positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) to keep airways open.
Airway Management Strategies
Maintain a clear and open airway. Use suction to remove secretions or obstructions. Consider inserting airway adjuncts like oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airways.
- Perform endotracheal intubation if ventilation remains inadequate.
- Reposition the head and neck to optimize airflow.
- Use bag-valve-mask ventilation for temporary support.
Pharmacologic Interventions
Medications may support breathing efforts and reduce airway resistance. Bronchodilators help relax airway muscles in cases of bronchospasm. Sedatives or paralytics may be needed during intubation.
- Administer epinephrine during severe airway obstruction or anaphylaxis.
- Use corticosteroids to reduce airway inflammation.
- Provide oxygen therapy to increase blood oxygen saturation.
Long-term Outcomes
Inadequate ventilation during pediatric advanced life support (PALS) can lead to serious long-term outcomes. The effects extend beyond the immediate emergency and can impact a child’s health for months or years. Understanding these outcomes helps caregivers and medical professionals prepare for ongoing care and recovery.
Potential Complications
- Brain damage due to low oxygen levels
- Chronic lung problems like scarring or infections
- Delayed growth and development
- Neurological disorders such as seizures or motor issues
- Heart problems caused by poor oxygen supply
Recovery And Rehabilitation
Recovery depends on the damage extent and timely treatment. Some children may regain full function, while others need ongoing support. Rehabilitation includes:
- Physical therapy to improve movement and strength
- Speech therapy for communication skills
- Occupational therapy to help daily activities
- Regular medical check-ups to monitor progress
Preventative Measures
Preventing inadequate ventilation is crucial for better outcomes. Proper training of healthcare providers on ventilation techniques saves lives. Use of monitoring devices ensures correct oxygen levels. Early detection of breathing problems allows faster intervention. Parents and caregivers should learn basic life support skills for emergencies.

Credit: quizlet.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Signs Of Inadequate Ventilation In Pals?
Inadequate ventilation in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) shows as low oxygen levels, increased carbon dioxide, and poor chest rise. Patients may appear cyanotic, have altered mental status, or show signs of respiratory distress. Early recognition is critical for effective intervention and improving outcomes.
How Does Inadequate Ventilation Affect Oxygen Delivery?
Poor ventilation reduces oxygen intake and carbon dioxide removal. This leads to hypoxia and respiratory acidosis, impairing tissue oxygenation. Without prompt correction, vital organs like the brain and heart may suffer damage, worsening patient prognosis and complicating resuscitation efforts.
Can Inadequate Ventilation Cause Cardiac Arrest In Children?
Yes, inadequate ventilation can lead to hypoxia, which stresses the heart and may cause cardiac arrest. In PALS, maintaining effective ventilation is essential to prevent respiratory failure and subsequent cardiac complications. Rapid correction helps stabilize the patient and improve survival chances.
What Interventions Improve Ventilation In Pals?
Interventions include airway positioning, suctioning, and using bag-valve-mask ventilation or advanced airway devices. Oxygen supplementation and continuous monitoring ensure adequate ventilation. Prompt adjustment based on patient response is vital for maintaining effective oxygenation and carbon dioxide elimination.
Conclusion
Poor ventilation affects health and comfort badly. Air becomes stale and full of harmful gases. Breathing issues and headaches may start to appear. Rooms feel damp, leading to mold growth. Mold can cause allergies and worsen asthma. Fixing ventilation helps keep air fresh and safe.
It also stops structural damage from moisture. Regular checks and simple changes make a big difference. Healthy air means better living and working spaces. Don’t ignore ventilation—it matters for well-being every day.