Have you ever wondered how fresh air keeps flowing in your home or workplace? Understanding ventilation is key to improving your comfort and health.
Knowing the three main types of ventilation can help you make smarter choices for your space. You’ll discover what these types are and how they work to keep the air clean and fresh around you. Keep reading—you might be surprised at how simple changes can make a big difference in your environment.
Credit: www.tejjy.com
Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation uses outdoor air to cool and refresh indoor spaces. It relies on natural forces like wind and temperature differences. This type of ventilation reduces the need for mechanical systems and saves energy. Natural ventilation can improve indoor air quality and comfort.
How Natural Ventilation Works
Natural ventilation works by moving air through openings in a building. Wind pushes air into the building through windows or vents. Warm air inside rises and escapes through higher openings. This creates a flow that brings fresh air inside and removes stale air.
Air moves from areas of high pressure to low pressure. Temperature differences also help air to circulate. Cooler air enters low openings, while warm air exits high openings. This cycle keeps the indoor air fresh without fans or machines.
Benefits Of Natural Ventilation
- Reduces energy costs by avoiding air conditioning.
- Improves indoor air quality by removing pollutants.
- Creates a comfortable indoor environment with fresh air.
- Helps control humidity and moisture levels.
- Quiet and low maintenance compared to mechanical systems.
Common Natural Ventilation Methods
- Cross Ventilation:Air flows through openings on opposite sides of a room.
- Stack Ventilation:Warm air rises and exits through high vents, drawing cooler air in below.
- Single-Sided Ventilation:Air enters and leaves through openings on one side, relying on wind pressure.
- Ventilation Through Courtyards:Open central spaces encourage air movement inside buildings.
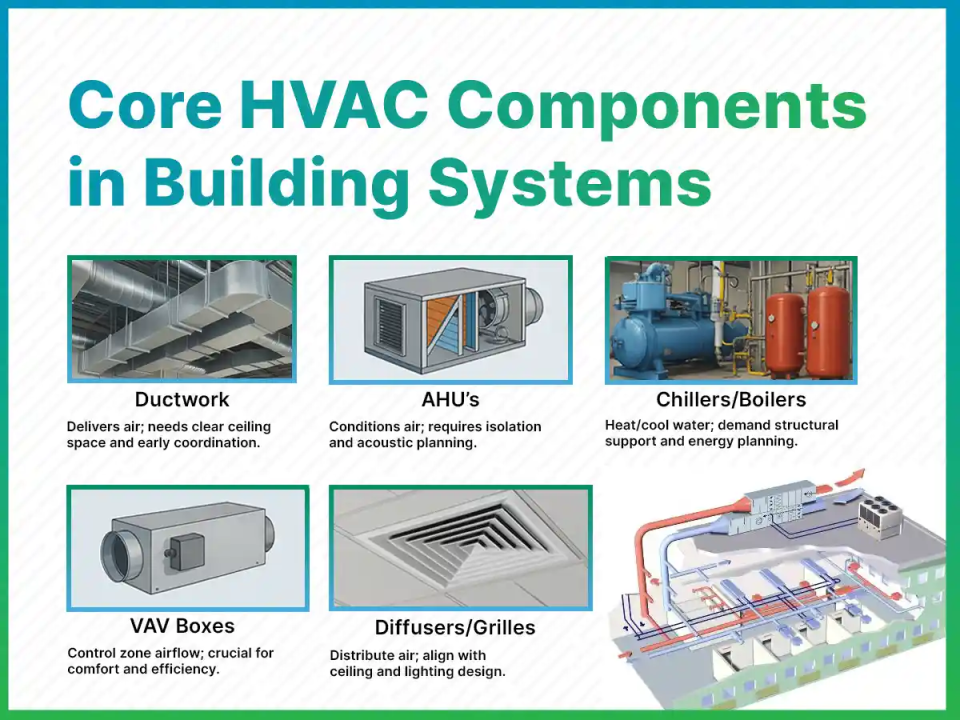
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation uses fans and ducts to move air in and out of buildings. It helps control indoor air quality by removing stale air and bringing fresh air inside. This system works well in tightly sealed homes where natural airflow is limited. Mechanical ventilation can be adjusted to meet specific needs, making it a flexible option for many spaces.
Types Of Mechanical Systems
- Exhaust Ventilation:Removes air from inside and lets fresh air enter through vents.
- Supply Ventilation:Pushes fresh air inside, forcing old air out through leaks or vents.
- Balanced Ventilation:Moves equal amounts of air in and out using fans, often with heat recovery.
Advantages Of Mechanical Ventilation
- Improves indoor air quality by controlling pollutants and humidity.
- Provides consistent airflow regardless of weather or building design.
- Reduces moisture buildup, preventing mold and damage.
- Allows for better control of temperature and comfort.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Mechanical ventilation systems can use energy, but some designs save power. Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) and Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) transfer heat between incoming and outgoing air. This process lowers heating and cooling costs. Proper system design and maintenance also improve energy efficiency. Choosing the right system helps balance fresh air needs with lower energy use.
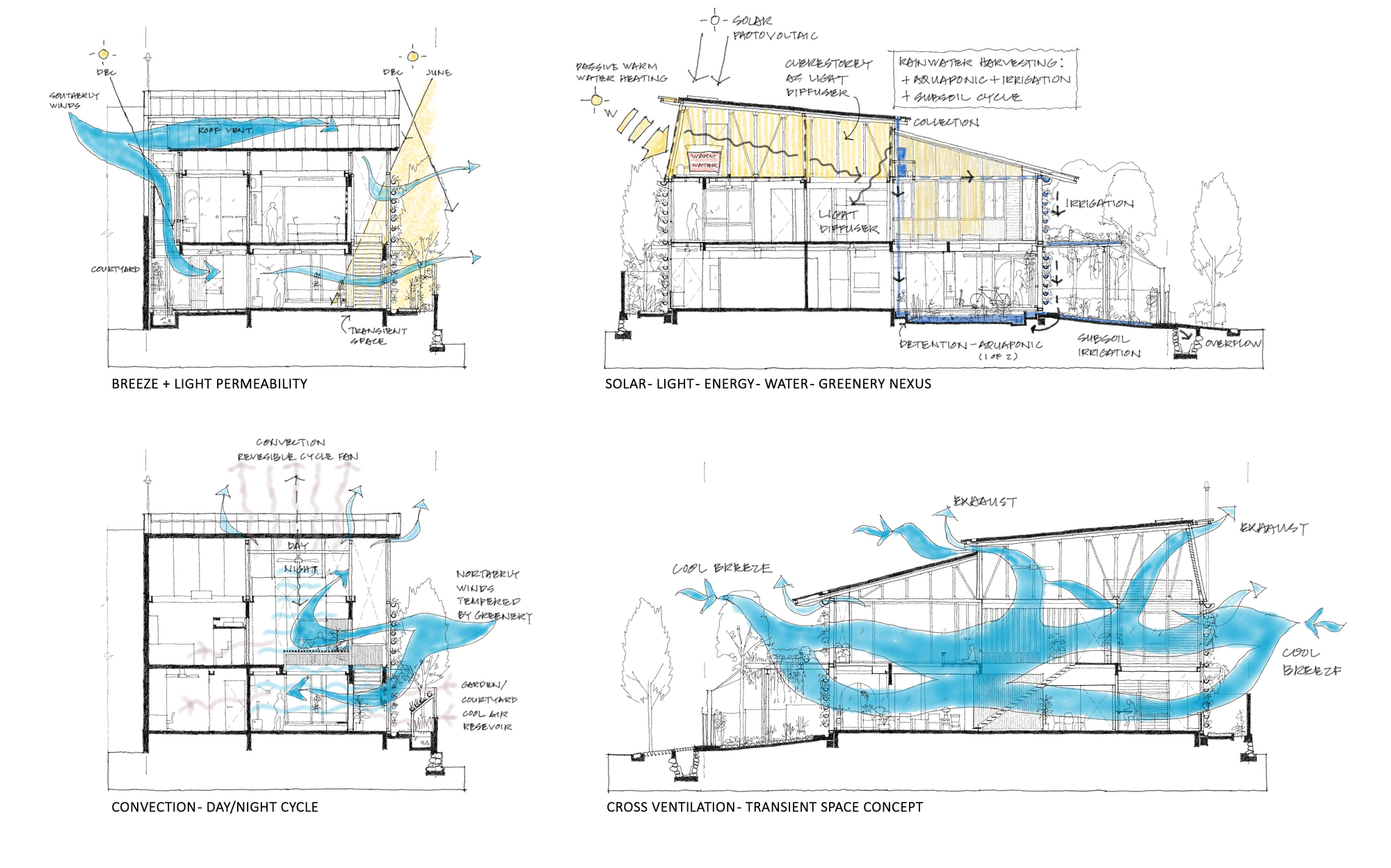
Hybrid Ventilation
Hybrid ventilation blends natural and mechanical methods to improve indoor air quality. This system uses outdoor air flow and fans or vents together. It adjusts automatically based on weather and building needs. Hybrid ventilation aims to save energy while keeping rooms fresh and comfortable.
Combining Natural And Mechanical
Natural ventilation uses wind and temperature differences to move air. Mechanical ventilation uses machines like fans or air exchangers. Hybrid systems combine both for the best results. They let fresh air in naturally when conditions are good. When outdoor air is poor or weather is bad, machines help circulate air.
When To Choose Hybrid Systems
Hybrid ventilation works well in climates with changing weather. It suits buildings with varying occupancy or air quality needs. Use hybrid systems in offices, schools, and homes for flexible control. This system adapts to different times of day and seasons. It keeps energy use low without sacrificing comfort.
Performance And Cost Factors
Hybrid ventilation can reduce energy bills by using natural air first. Mechanical parts use electricity only when needed. Installation costs are higher than simple natural or mechanical systems. Maintenance involves checking both natural openings and mechanical equipment. Over time, energy savings can balance initial expenses.
Credit: illustrarch.com
Choosing The Right Ventilation
Choosing the right ventilation system is key for a healthy home. It affects comfort, energy use, and air quality. Different homes need different types of ventilation. Think about your home’s size, location, and typical weather. Each ventilation type has its benefits and limits. Understanding these helps you pick the best one.
Factors To Consider For Homes
Start with your home’s size and layout. Small homes might work well with simple systems. Larger homes may need more powerful ventilation. Consider your climate too. Humid places need systems that reduce moisture. Cold climates need ventilation that keeps heat inside.
Noise level is important. Some fans are quieter than others. Think about installation cost and energy use. Choose a system that fits your budget long term. Also, check if your home has existing ducts or vents.
Impact On Indoor Air Quality
Good ventilation removes stale air and brings fresh air inside. This lowers dust, allergens, and harmful gases. Some systems filter incoming air better than others. A system that controls humidity helps prevent mold and mildew. Proper airflow also reduces odors and keeps rooms fresh.
Balanced ventilation systems offer fresh air without losing too much heat. They keep indoor air cleaner and healthier. Poor ventilation can cause stuffy rooms and health problems.
Maintenance And Longevity
Choose a system that is easy to maintain. Filters need regular cleaning or replacement. Fans and vents should be checked for dust build-up. Some systems last longer with less upkeep. Look for durable materials and reliable brands.
Regular maintenance keeps the system working well. This saves money on repairs and energy bills. A well-maintained ventilation system works efficiently for years.

Credit: www.jacc.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Types Of Ventilation Systems?
The three main types of ventilation are natural, mechanical, and hybrid ventilation. Each type controls airflow to maintain indoor air quality effectively.
How Does Natural Ventilation Work In Buildings?
Natural ventilation uses wind and temperature differences to move fresh air inside. It relies on openings like windows and vents for airflow.
What Is Mechanical Ventilation And Its Benefits?
Mechanical ventilation uses fans and ducts to circulate air. It ensures consistent airflow and controls humidity and pollutants indoors.
When Is Hybrid Ventilation Recommended?
Hybrid ventilation combines natural and mechanical methods. It is ideal for energy efficiency and maintaining air quality in varying weather.
Conclusion
Good ventilation keeps air fresh and healthy indoors. The three types—natural, mechanical, and hybrid—each serve a unique purpose. Natural ventilation uses windows and vents to bring in fresh air. Mechanical ventilation relies on fans and machines for airflow. Hybrid combines both methods for better control.
Choosing the right type helps reduce moisture, odors, and indoor pollution. Understand these options to improve your home or office air quality. Clean air supports comfort and well-being every day. Remember, proper ventilation matters for a healthier living space.





